Comparing Different Image Formats for the Web

Those who work on the internet know well how image formats are essential. Whether it be a photograph or a graphic element, there are many alternatives to choose from. The suggestions are clear and known to anyone, but the characteristics vary from format into format. For this reason, it can be easy to fall into confusion. So how can we choose the right image format?
Before starting, it's good to be clear about something: the perfect image format doesn't exist. It depends on what your needs are: are you trying to save space, and improve load times? Do you need a high quality, editable image? Do you want an animation? So let's see how all the most used formats has pros and cons depending on how the user will implement them online.
JPG
The JPG format, acronym of Joint Photographic Experts Group, is most certainly the best-known one. This standard format was created to obtain files that take up very little storage space while maintaining good quality. The way it works it's truly simple: JPG removes all those details that are not immediately recognised by the human eye, reducing the file size. That's why it's called a "lossy" format.
The main advantage, besides taking very little storage space, is the extended compatibility with any software and devices nowadays virtually existing. The disadvantage is that the quality of this image format can be brutally lowered as a consequence of harsh compression. Not to forget that JPG format doesn't support transparency.
Check the two pictures below:
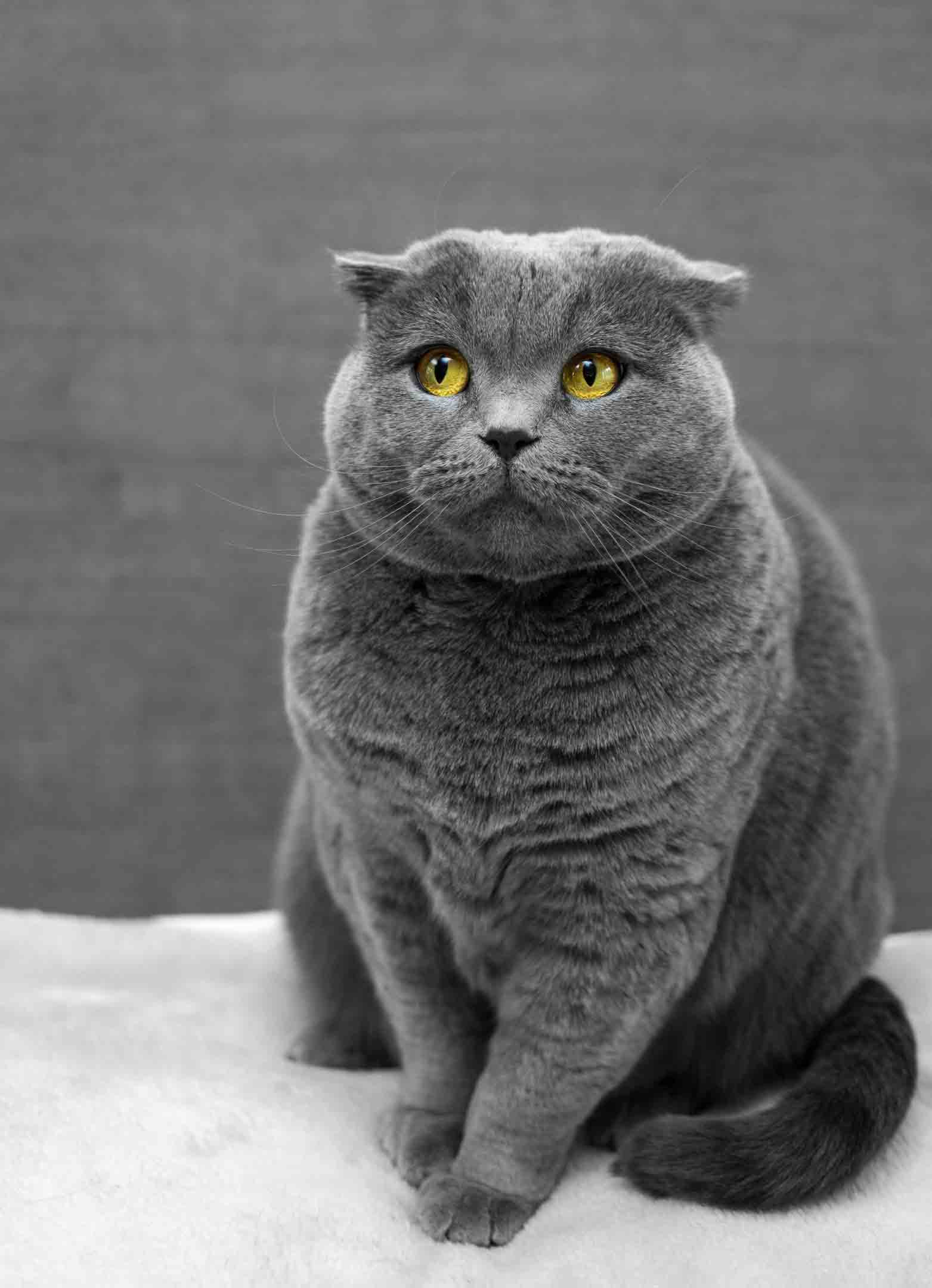


It's difficult, if not almost impossible to spot the differences. But the compression really makes a lot of difference: the size of the first image is 368 KB while the second is only 81 KB thanks to the hard compression.
PNG
Very similar to JPG, the PNG format - acronym of Portable Network Graphics - grants high-quality images
maintaining a moderate small file size, even though most of the times can result larger than JPG.
PNG is "lossless", meaning that you do not lose any data during compression. This image format is mostly used
for static images; however, they can support animation.
The great advantage is the full support of transparency, useful when dealing with graphic elements.
The disadvantages are: larger file size for images and, although rare, incompatibility for some software.
However, PNG images are gaining great consent on the social networks where they often turn out to be the user’s first choice. Platforms like Facebook, for example, tend to compress JPG files further once the user uploads them, resulting in a drastically lower quality image. This doesn't happen with PNG, as it ensures the user to view a picture as it was meant to be originally.

GIF
Popular in the 90s, the GIF format - Graphics Interchange Format - was fished out from the oblivion and then revalued and proposed with social networks. GIFs are "lossless", they retain all the data contained in the file. This standard is ideal for short animations. As a matter of fact, it allows us to put together multiple frames and then to repeat it in a loop, creating a sort of video. It supports transparency and nowadays is widely used in social platforms.
Although more powerful formats exist these days, the main advantage of GIF consists of his virality. Who hasn't ever had fun with these great bouncy animations? The most known platforms now all support GIF as a mean to share files between users! The disadvantage is the low image quality and the file size that can get quite cumbersome for long animations. Nowadays, it's widely implemented in all messaging software.
SVG
I love SVG! This format is gaining more and more popularity. Scalable Vector Graphics are a type of file based on vectors: simply put, SVGs can be resized at any level without losing any of the visual quality. That's because an SVG is drawn from mathematically declared shapes and curves, not pixels. Not by chance is the preferred format for HTML 5 animations. SVG is a "lossless" file format like GIF and PNG.
The great advantage consists in his versatility. In fact, SVGs scale authomatically; they allow to design interfaces or graphic elements regardless of the resolution and size of the device. The disadvantage is the fact that the most popular social media platforms do not fully support SVG. They can also be fairly large files to deal with.

HEIF, BMP and more
There are many images formats. To list them all, it would be almost impossible. However, there are a few options to keep in mind. Starting from the new HEIF, the format that could replace JPG in the future. HEIF was created to garantee high quality on light file size, with a more efficient compression than the classic JPG. At the moment, it's supported on all the latest Apple devices and most of the browsers, but it still doesn't seem to be spreading widely any time soon.
BMP deserves to be mentioned, as it was one of the first image formats that brought images on the digital world. Today is almost in disuse, apart for particular printing purposes. We can list TIFF for printing and typographical purposes, PDF for document and many more.
So what image format should you use? If you're uploading pictures to Facebook, JPG is the winner. You want to make a short, hilarious animation from your favourite movie scene? GIF. If you're going to be using high-quality images, detailed icons or need to preserve transparency, PNG is the winner. SVG is ideal for high-quality images and can be scaled to ANY size.